



General
The airways must be protected from a number of hazards that may be present in the workplace:
- Chemical hazards in the form of gases, vapours, dust, mists, and aerosols.
- Thermal hazards, such as hot or cold air currents.
- Suffocation due to lack of oxygen in a space filled with nitrogen.
- Risk of contagion due to biological hazards.
Respiratory protective equipment makes sure that inhaled air is free of harmful contamination, and does not pose a danger to workers’ health. Unprotected inhalation of hazardous substances can lead to temporary or permanent injury, or even death.
In addition to acute risks, respiratory protective equipment protects you against long-term risks.
There are two main groups of respiratory protective equipment: respirators and breathing apparatus.
- Breathing apparatus uses an external air supply. The respiratory air can be sent to the worker from outside the workplace via a hose, or the air can be carried in a pressurised cylinder worn by the worker.
- Respirators, on the other hand, are masks, helmets or hoods which filter ambient air in combination with a gas and vapour and/or dust filtration system, so that contaminants stay below the limits allowed in the workplace.
A Risk Inventory and Evaluation (RI&E) must be carried out to determine the protective equipment used. Initially, it should be determined whether any hazards can be prevented in another way by removing the ‘source’, or using technical/organisational measures. If such measures are not possible, respiratory protection must be used to prevent damage to health. The RI&E must specifically determine whether the circumstances demand respirators or breathing apparatus.
Breathing apparatus
Before using breathing apparatus, workers must first undergo medical examinations and training. Usage/protection in the following situations1:
- Oxygen level less than 18% or greater than 21%;
- Dust/vapour concentrations more than 40 times the limit and/or above 1% by volume; 2
- Gases above limit values;
- Confined areas;
- Substances for which there are no suitable filters, such as butane, methyl chloride, argon and natural gas.3
Respirators
Usage/protection in the following situations:
- Oxygen level between 18% and 21%;
- Where breathing apparatus criteria do not apply
There are masks for dust/aerosols, and masks for gases, vapours and mist (often combined with dust filter)
Disposable dust mask
Usage/protection in the following situations: Dust, substances, aerosols
P1: harmless substance (limit value 10 mg/m3 or more)
P2: harmful substance (0.1 < limit value < 10 mg/m3)
P3: toxic or CMR *4 substance (limit value < 0.1 mg/m3)
Uniper Benelux only provides P3 dust masks.
Uniper Benelux nv provides the following types of P3 masks:
- 3M Type 8835
Half or full-face mask with filter cartridge
Usage/protection in the following situations: Gases, vapours, mist and substances ABEKx Px = combination of gas/vapour and dust filter with class x = 1, 2, 3 2
At Uniper Benelux nv, the following types of half masks and full-face masks are used:
- 3M 4251 half-face mask
- 3M 6100 S half-face mask
- 3M 6200 M half-face mask
- 3M 6300 L half-face mask
- 3M 9925 welding fume half-face mask
- 3M 6800 S full-face mask
- 3M 6900 M full-face mask
Accessories:
- 3M 105 mask cleaner
Filter types:
- A (brown): hydrocarbons, boiling point > 65 ºC
- AX (brown): hydrocarbons, boiling point < 65 ºC
- B (grey): acid gases, such as chlorine
- E (yellow): sulphur dioxide
- K (green): ammonia
- P3: dust
There are also specific cartridges for:
- NOx (blue): nitrous vapour
- CO (black) *5: carbon monoxide
- Hg (red): mercury vapour
The following filters are used at Uniper:
- 3M A1 filter 6051
- 3M A1 filter 6000
- 3M P3 filter 8835
- 3M P3 filter 2135
Combination with eye protection
If both respirators and full-face protection are required (such as with acid splashes), either a full face mask or a face screen with chin in combination with a P3 filter mask are possible.
Facial hair
Facial hair more than a few millimetres long (beards and moustaches) will stop masks working properly, due to poor sealing. Protection is not guaranteed. A Van Der Grinten mask with ventilation unit is a suitable alternative.
Maintenance of masks
Half-face masks/full-face masks: After every use(!), clean the mask with special cleaning cloths, and store in a suitable bag.
Expiry date (UGD) and duration of use/saturation of filters
The expiry date (UGD) is stated on the filter or its packaging. Never use filters beyond their expiry dates.
Disposable and other P3 filter masks are saturated if breathing resistance can be felt in the mask. The filter must be replaced immediately. If a disposable P3 filter mask has to be worn for several hours, replacing the filter every 2 hours or every break is recommended.
For gas/vapour filters, the saturation time is difficult to determine, since it depends largely on concentrations in the air. As soon as the gas/vapour can be smelled, the filter must be replaced. Respirators are therefore not permitted for odourless gases. This does not apply to the CO emergency escape mask. If the supplier is informed about concentrations in the air and usage time, an estimate of the saturation time can be requested.
Half-face mask and full-face masks used daily must be replaced at least every six months.
Storage and disposal of masks and filters
Keep masks in a dry, cool, dark and dust-free place, such as in a clean sealed plastic bag.
Dispose of P3 masks as chemical waste after single use. Single use is understood to be from a few seconds to a maximum of 8 hours or 1 workday.
Dispose of saturated filters as chemical waste. Respect the expiry date of the filter on the packaging.
1 The maximum time that breathing apparatus may be worn is 2 hours for light work or 30 minutes for heavy work, followed by a rest period of 20 minutes.
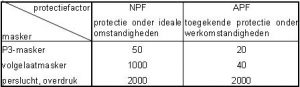
2 The higher the x, the higher the protection factor. The assigned protection factor (APF) of a full-face mask = 40 times the limit value, and of a P3 disposable mask = 20 times the limit value, see table. In addition, there are gas/vapour filters with 3 capacity classes: class 1 (up to 0.1 vol% = 1,000 ppm), class 2 (up to 0.5% = 5,000 ppm), class 3 (up to 0.8 vol. % = 8,000 ppm). The assigned protection factor of the mask is what counts!
3 Asphyxiant and noble gases that suffocate, and with substances that are very difficult for the filter to absorb.
4 For a CMR substance (Carcinogenic, Mutagenic or Reprotoxic substance), a P3 full-face mask offers twice as much protection (APF) as a P3 mask, see the table below.
5 A CO filter mask is only allowed as an escape mask in an emergency. In all other cases: breathing apparatus.
6 Extracting air for respiratory protection from the instrument pneumatic network is prohibited.